Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
This diagram illustrates the effects of a production subsidy, where the government supports domestic producers to lower their costs and increase output. It is a form of protectionism without raising consumer prices directly.
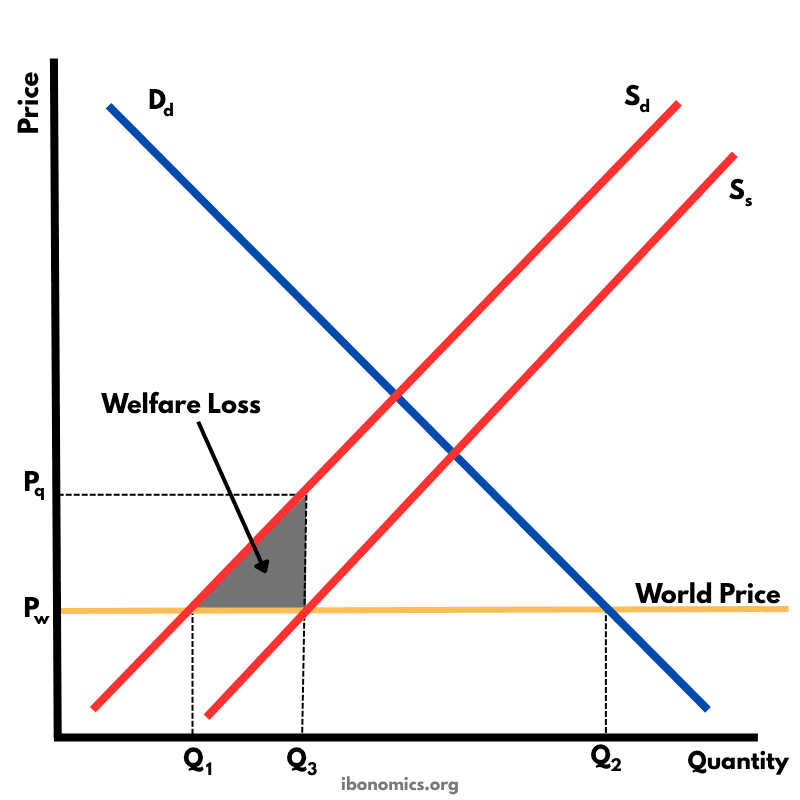
Dd: Domestic demand for the good.
Sd: Original domestic supply curve.
Ss: New domestic supply curve after subsidy, showing increased output.
Pw: World price of the good, unchanged by the subsidy.
Pq: Price received by producers.
Q1: Domestic output under free trade.
Q3: Domestic output after subsidy.
Q2: Total quantity demanded at world price.
Welfare Loss: Grey area showing inefficiencies from producing beyond the comparative advantage level with government support.
Under free trade, domestic producers supply Q1, and the remaining demand is fulfilled through imports (Q2 - Q1) at the world price Pw.
A production subsidy shifts the domestic supply curve from Sd to Ss, reducing production costs and allowing domestic firms to expand output from Q1 to Q3.
Imports fall from (Q2 - Q1) to (Q2 - Q3) as domestic output replaces part of the imported quantity.
The domestic price remains at Pw, so consumers are unaffected directly; however, the government must fund the subsidy.
A welfare loss arises due to inefficient allocation of resources, as subsidy-induced domestic production exceeds the efficient free trade level.
Explore other diagrams from the same unit to deepen your understanding
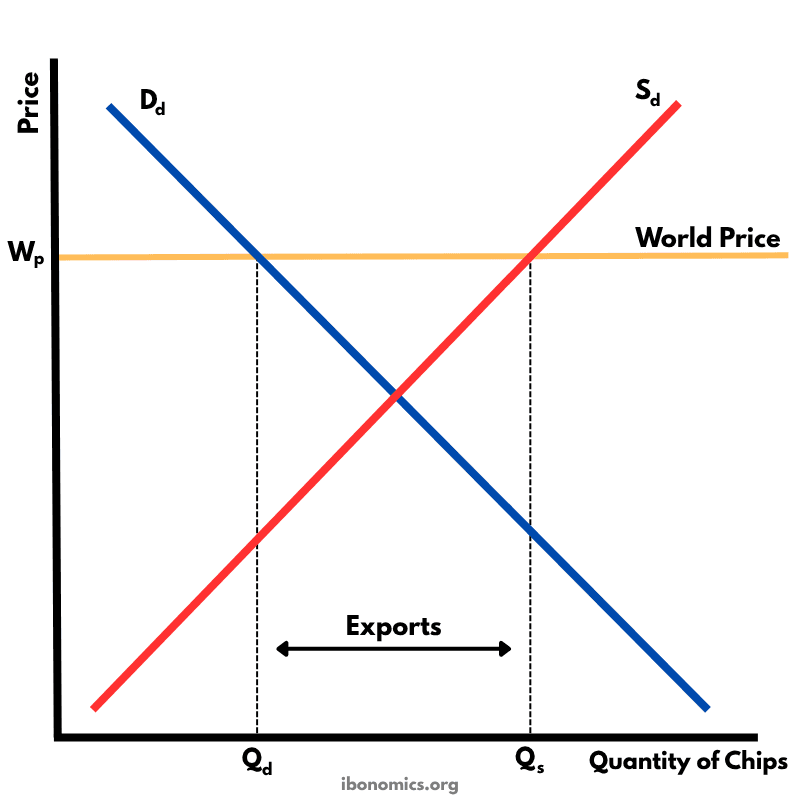
This diagram shows how a country exports goods under free trade when the world price is higher than the domestic equilibrium price.
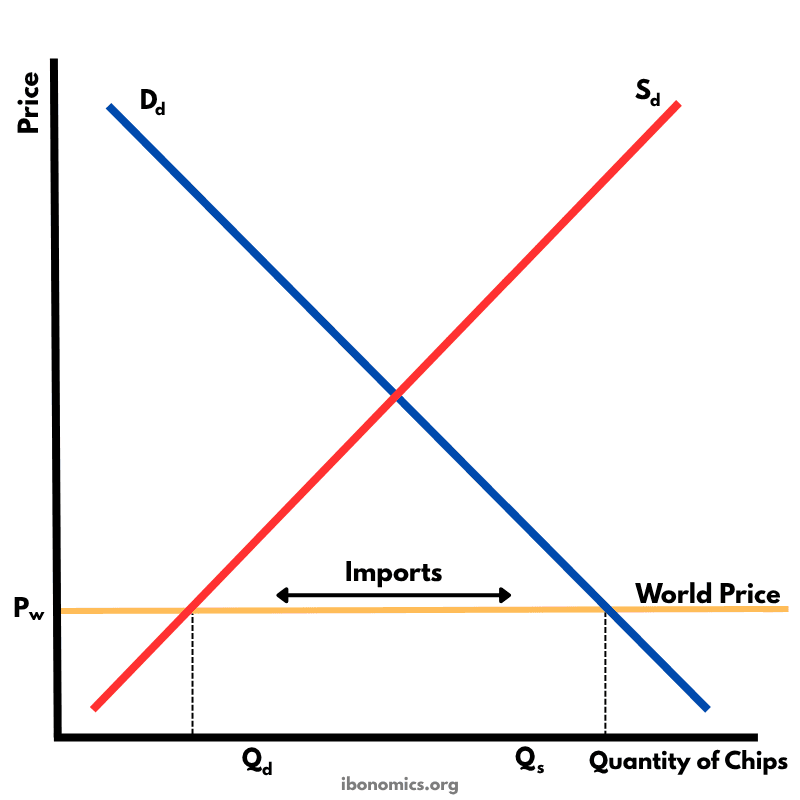
This diagram illustrates how a country imports goods under free trade when the world price is lower than the domestic equilibrium price.
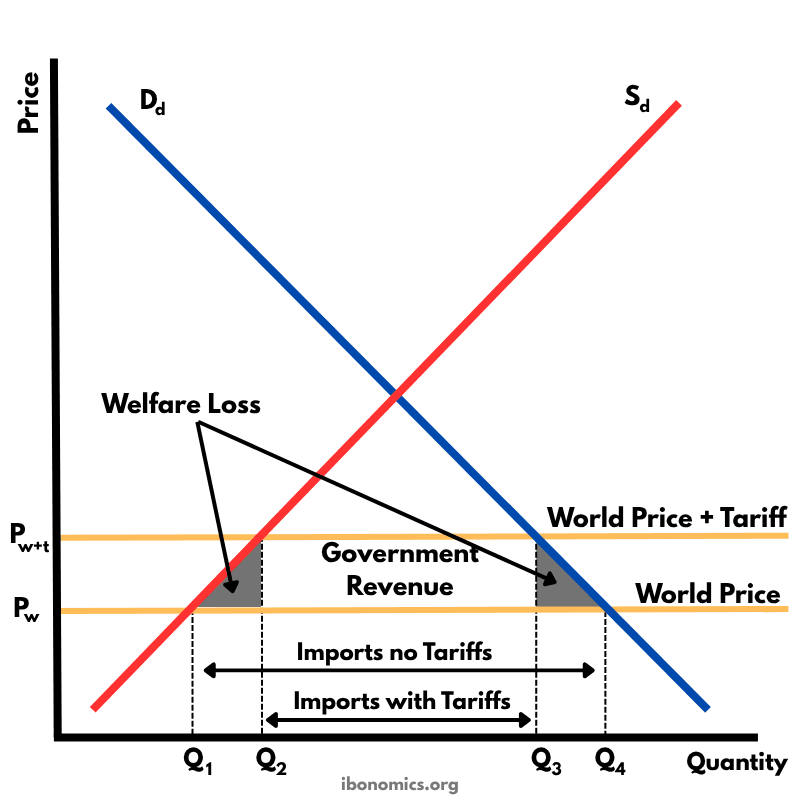
This diagram shows the effects of a tariff imposed on imported goods. A tariff raises the price of imports, protecting domestic producers but creating welfare losses.

This diagram shows the impact of an import quota that limits how many units of a good can be imported. By restricting imports, the domestic price rises above the world price, domestic producers expand output, consumers buy less, and there is a net welfare loss.
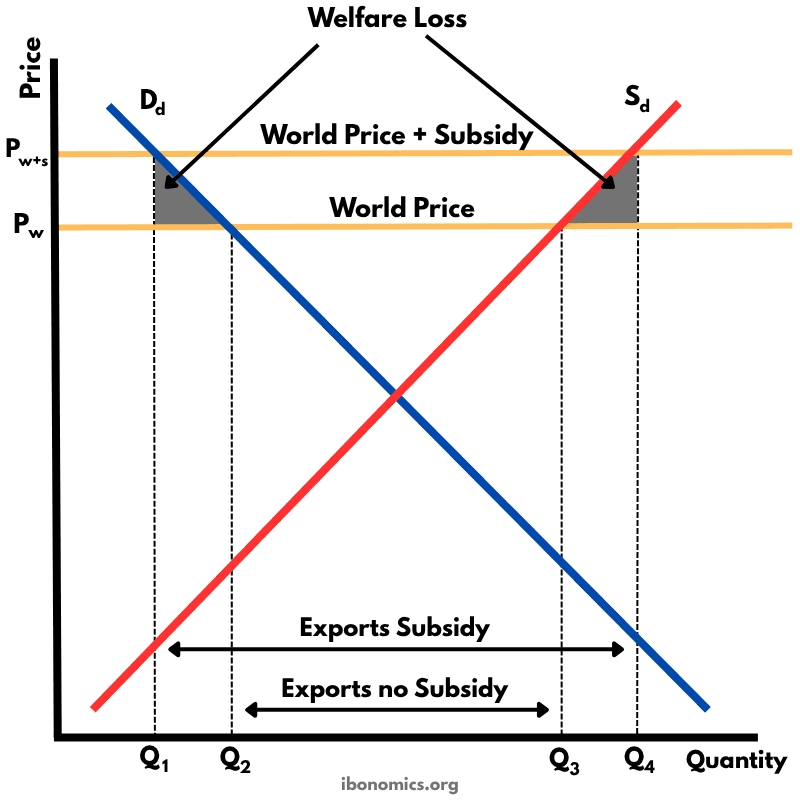
This diagram shows how an export subsidy raises the domestic price above the world price, encouraging producers to export more while reducing consumer welfare and creating deadweight losses.
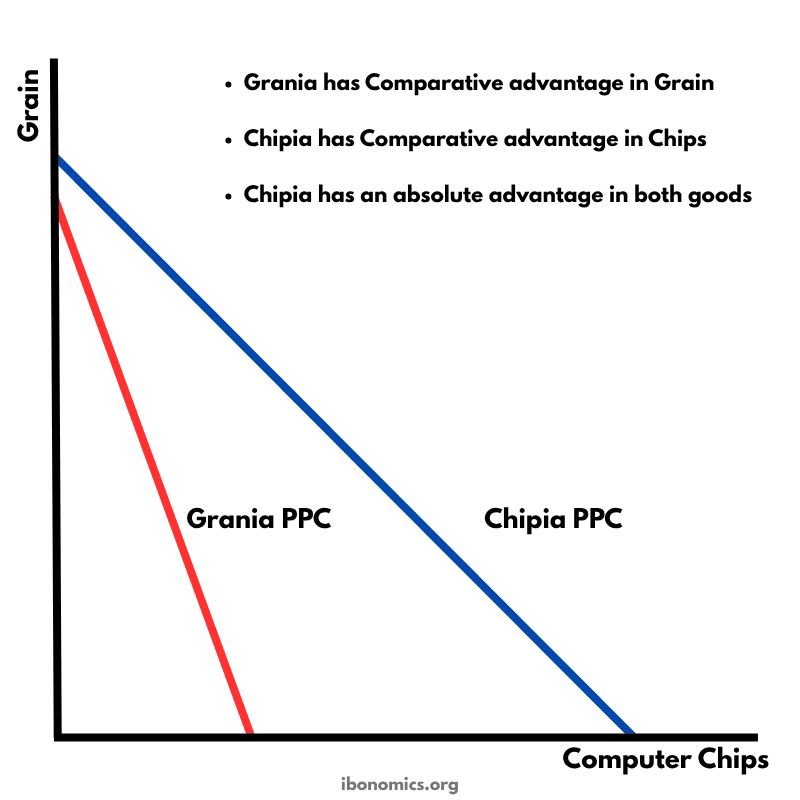
This diagram uses production possibility curves (PPCs) for two countries—Grania and Chipia—to illustrate absolute and comparative advantage and the potential gains from trade.